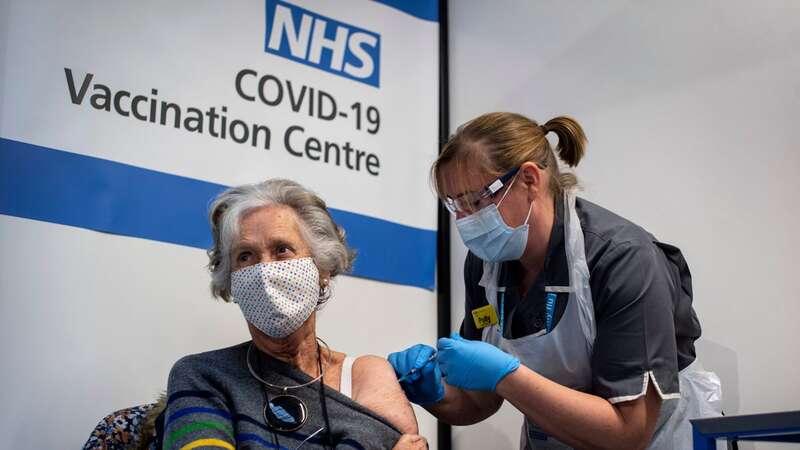

Health chiefs in the UK have been keeping a close eye on a new Covid variant that led to them bringing forward the autumn vaccination programme.
BA.2.86, nicknamed Pirola, had fewer than 40 confirmed cases by the end of August and most of those were in a single care home in Norfolk. Despite these seemingly low numbers, the variant led to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) rushing forward its autumn booster jab programme by about three weeks, in an effort to give the country the best chance possible of avoiding any major outbreaks.
Alongside that, it's been keeping a close eye on the variant and publicly followed it far more than any variant since Omicron. One of the key reasons that Pirola has caught the attention so keenly is due to the 30 mutations on its spike protein. This has raised concerns that vaccines which target the spike may prove ineffective at cheating antibodies.
So far, there has been no evidence that BA.2.86 is more dangerous or transmissible than past variants.
Care home outbreak
The Norfolk care home registered 28 cases in a single outbreak last month, leading to mass testing inside which confirmed that Pirola was responsible for the majority of cases, according to UKHSA.
 Spectacular New Year fireworks light up London sky as huge crowds celebrate across UK for first time in three years
Spectacular New Year fireworks light up London sky as huge crowds celebrate across UK for first time in three years
Dr Renu Bindra, Incident Director, UKHSA said: “While BA.2.86 has a significant number of mutations to the viral genome compared to other currently circulating COVID-19 variants, the data so far is too limited to draw firm conclusions about the impact this will have on the transmissibility, severity or immune escape properties of the virus.
“Specialists from UKHSA have been working with Norfolk County Council to offer infection control advice and support following a confirmed outbreak of BA.2.86 in a care home. It is clear that there is some degree of widespread community transmission, both in the UK and globally, and we are working to ascertain the full extent of this. In the meantime, it remains vital that all those eligible come forward to receive their autumn vaccine as soon as it is offered to them.”
This continues to account for the majority of UK cases but has raised alarm because it has shown the new variant can transmit in close quarters.
Vaccination programme brought forward
The government and UKHSA brought forward the autumn booster jab programme by around three weeks because of Pirola. Whilst not yet a Variant of Concern, it has done enough to warrant this action.
Now, combined with the annual winter flu surge, the country could face a twindemic of both viruses. In response, the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) quickly brought forward its vaccination programme, seeing as there has been an outbreak in a Norfolk care home, that saw all 34 cases confirmed to be BA.2.86.
People eligible for the booster jab:
Care home residents
All adults aged 65 and older
People aged six months to 64 in a clinical risk group, this includes pregnant women, people with diabetes, obesity and more - visit the UKHSA for the full list of those in the clinical risk group
Frontline health and social workers
People aged 12 to 64 who live with people with weakened immune systems
 Hospitals run out of oxygen and mortuaries full amid NHS chaos
Hospitals run out of oxygen and mortuaries full amid NHS chaos
People aged 16 to 64 who are carers and/or staff working in care homes for older adults
What are the symptoms of Pirola?
So far, there does not appear to have been any observed symptoms that are out of the ordinary when it comes to Covid.
The key signs are what you might expect from Covid, including:
- Sore throat
- Cough (with or without phlegm)
- Headaches
- Runny or blocked nose
The picture across the home nations and beyond
So far, there have been seven hospitalisations, and two cases in emergency departments, and no deaths from the variant, but there has been no evidence of it being brought in from abroad, suggesting a level of community transmission.
Alongside that, a study of BA.2.86’s phylogeny and evolutionary history suggested it was introduced to the UK on a number of separate occasions.
As of September 11, England had 37 sequenced cases, an increase of three on the week before. These were present in the east of England, London, North East and North West.
Meanwhile, Scotland has recorded five cases and Wales and Northern Ireland are yet to record the variant.
The global situation of BA.2.86 was defined as “dynamic” by UKHSA, who said there were 99 sequences by September 12, from 14 countries according to GISAID. The earliest was identified on July 24, with the UK representing over a third of sequences.
In some countries, BA.2.86 has been found in wastewaters as well; for example, Thailand, which is yet to confirm a case.
The variant has been found in the following countries: Australia (1); Canada (2); Denmark (13); France (7); Germany (1); Israel (3); Japan (1); Portugal (2); South Africa (17); South Korea (1); Spain (4); Sweden (5); UK (36); and USA (7).