BEING fat can swell a vital part of your brain and send food cravings spiralling out of control, a study suggests.
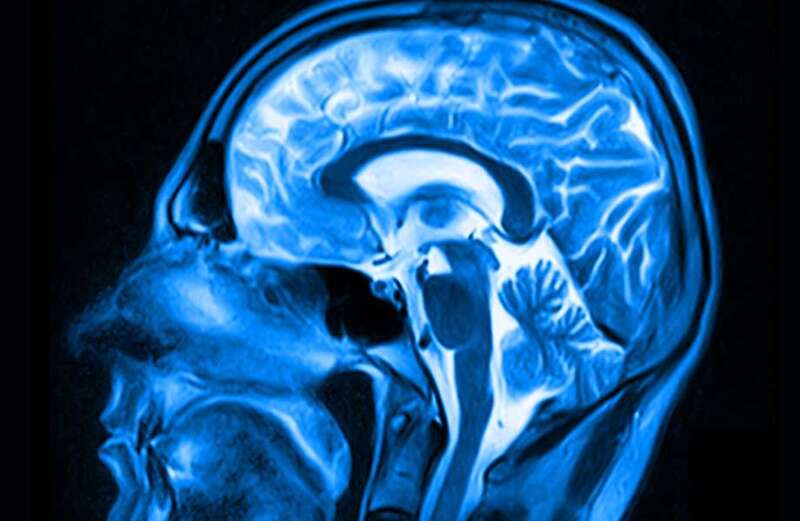
Cambridge University scientists used head scans to find overweight people have a bigger hypothalamus.

The brain region is only about the size of a pea but is key to controlling appetite and sending fullness signals to stop you eating.
Long-term inflammation in this grey matter can send it haywire, experts say.
Study author Dr Stephanie Brown said: “Eating a high-fat diet could trigger inflammation of our appetite control centre.
 From tongue scraping to saying no, here are 12 health trends to try in 2023
From tongue scraping to saying no, here are 12 health trends to try in 2023
“Over time, this would change our ability to tell when we’ve eaten enough.
“It could also change how our body processes blood sugar, leading us to put on weight.”
Two in three Brits are overweight and half of them are obese.
Carrying the extra pounds raises the risk of deadly illnesses like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, cancer and stroke.
The study, published in the journal Neuroimage: Clinical, analysed MRI brain scans from 1,351 people.
It compared the size of the hypothalamus in people of different weights and found it “significantly increased” in fatter participants.
The scientists noticed that the parts that increased most in size were the ones linked directly to controlling hunger.
They said they cannot prove whether the swelling is caused by excess flab or it comes first and drives people to eat more.
But mouse studies show that normal rodent brains begin to swell after just three days of eating a fatty diet.
Dr Brown added: “We know the hypothalamus is important for determining how much we eat but we actually have very little information about it because it is small and hard to see on scans.”
 I'm a nutritionist - here's the 10 best diet trends to help lose weight in 2023
I'm a nutritionist - here's the 10 best diet trends to help lose weight in 2023